Overview
What is a 2.5D workflow?
2.5D workflows bridge the gap between traditional 2D video plates and full 3D generative scenes. By building up a scene with layers of images or video plates, with the possibility to add depth or shaping to the plates, users can quickly create a realistic looking scene with parallax. 2.5D assets can be saved as .2p5d files and shared across projects, or created using external integrations such as Cuebric to harness the power of generative AI.
See How It Works
Workflow
This section details the following how-to guides:
-
Set up a 2.5D asset from an existing .2p5D file
-
Create a new 2.5D asset from scratch
-
Modify 2.5D asset properties
-
Modify 2.5D plate properties
-
Advanced workflows
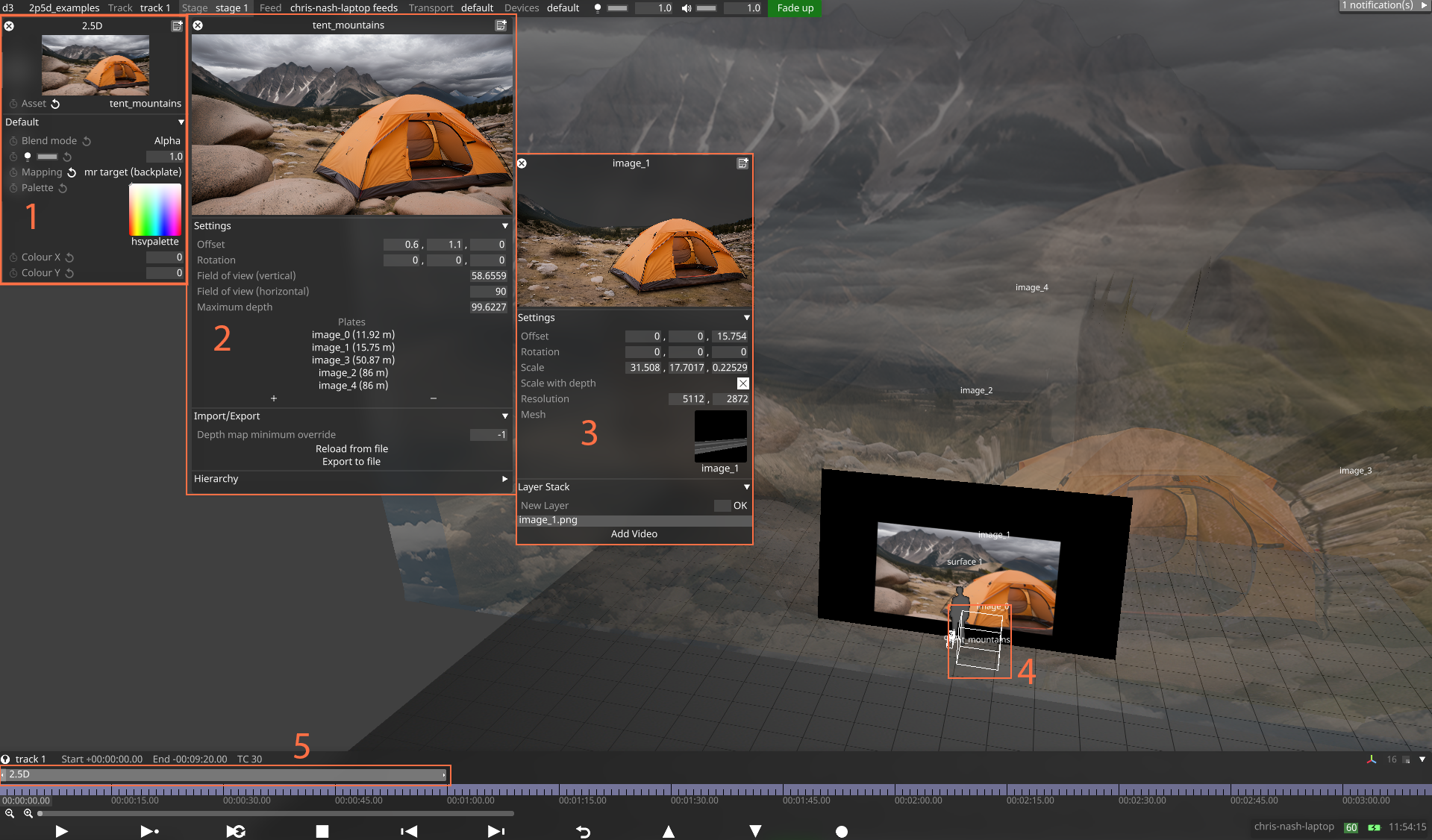
Key
-
2.5D Layer editor
-
2.5D Asset editor
-
2.5D Plate editor
-
2.5D Asset origin
-
2.5D Layer
Set up a 2.5D asset from an existing .2p5D file
-
Copy the .2p5d file to objects/2p5DFile in the project folder.
-
Add a 2.5D layer to the timeline.
-
In the 2.5D layer editor, click on the Asset field. The copied 2p5d file should appear in the list of assets in the 2.5DAsset selector.
-
Click on the asset to select it. It will then load and be visible in the stage.
-
In the 2.5D layer editor Mapping property, select the desired 3D mapping e.g. MR set backplate.
-
To reload the asset from file and overwrite any local changes, click Import/Export > Reload from file in the property editor of the 2.5D asset.
Create a new 2.5D asset from scratch
-
Add a 2.5D layer to the timeline.
-
In the 2.5D layer editor, click on the asset field and create a new 2.5D asset.
-
Add a new 2.5D plate to the plates field in the 2.5D asset.
-
Under Layer Stack in the plate editor, click Add Video to add a video or image to the plate.
-
Continue adding plates and modifying their properties until the desired scene composition is achieved.
-
Select the desired 3D mapping in the 2.5D layer, e.g. MR set backplate.
-
To export the asset for use in other projects, click Export to file under Import/Export in the 2.5D asset editor. The exported .2p5d file will appear under objects/2p5DFile in the project folder.
Modify 2.5D asset properties
-
The 2.5D asset is an Object which can have its offset and rotation set by changing the values in the editor, or moving the 2.5D Asset origin (white box) in the visualiser. Doing so will move all the plates and change the origin point of the 2.5D scene. It is recommended that the origin is set roughly in the middle of the range of movement of the camera, to achieve the most realistic looking parallax.
-
The Field of view and Maximum depth fields can be adjusted to scale the total area encompassed by the 2.5D scene. This can be used to ensure that the edges of the plates are not seen when moving the camera within its expected range.
-
Plates can be added to or removed from the asset using the +/- buttons in the Plates field of the asset editor. Plates are ordered by depth, and reordering the plates in the list will update the plates' depth to reflect their new positions.
-
The Import/Export settings can be used to load or save .2p5d files. When loading files which contain depth maps, the Depth map minimum override setting can be used to change the minimum distance from the origin, represented by full white in the depth map.
Modify 2.5D plate properties
-
The plate depth can be changed by modifying the z offset value, or by dragging the plate in the visualiser. If the option Scale with depth is ticked, the scale and x/y offsets will automatically be adjusted with depth so that the plate looks the same when viewed from the asset origin. If Scale with depth is not ticked, the scale and x/y offsets will not change, so the plate will appear smaller as it moves further away.
-
By default, new plates will be scaled to match the total field of view of the asset. However, the scale values can be adjusted in the 2.5D plate editor to change the scale. Similarly, the x and y offsets can be adjusted to move the plate position.
-
The plate’s mesh can be changed to add depth to a layer and make the parallax effect more realistic. Some .2p5d files will contain depth maps, which will be converted to meshes when importing. To remove the depth from the plate, the standard rectangle mesh can be selected instead.
-
The plate Layer Stack is used to set up the layers appearing on the plate. To quickly add an image or video to the plate, use the Add Video button. Otherwise, layers can be created as normal and stacked to create effects such as blur or colour adjust. Note that these layers can’t be keyframed, see Advanced Workflows for methods to keyframe layers on plates.
Advanced workflows
The 2.5D layer and assets are designed to provide a user-friendly way to quickly create 2.5D scenes which are portable between projects. The standard workflow should allow for the majority of use-cases, however more advanced workflows can also be achieved by combining 2.5D assets with other tools in Designer.
-
Generally images, videos and effects should be added to plates using the plate Layer Stack. However, this does not allow for keyframing within these layers. To keyframe content on plates, layers should be added to the timeline as normal. Content can be mapped to 2.5D plates from the timeline similarly to any other display.
-
2.5D assets and plates are both Objects, so it is possible to animate them from the timeline, or parent assets to other objects which are controlled using tracking data
-
The Stage render layer which was used for 2.5D workflows prior to r26.3 still functions as it did previously, so it is still possible to use the original workflow if desired.
Original workflow (availabe prior to r26.3)
-
Using the stage menu, add an LED surface and a camera to your project.
-
Create 3 projection surfaces and position them behind the LED screen incrementally with a gap of several metres between each.
-
Label each surface in the composition stack to reflect it’s location. e.g. "foreground', "midground", and 'background".
-
Make the following changes:
-
Set foreground and midground surfaces to Transparent
-
Set the blend mode for the foreground and midground to Alpha.
-
Change the render layer of each surface to Backplate (MR).
-
-
Using the stage menu, create an MRset.
-
Assign the LED screen to the MRset and change the Camera property to Camera override.
-
Add a StageRender layer to the timeline above the other content layers and map it to the backplate.
-
Move the camera within the MRset to activate it.
-
The perspective projection will appear on the LED screen and tracks the movement of the camera.
Further Reading