Colour Shift
The colour shift property allows you to perform a number of colour-correction operations on the output of a layer.
Colour Shift objects can also be attached to individual video files within the Video layer.
 Colour Shift property performs colour-corrections on the output of a visual layer
Colour Shift property performs colour-corrections on the output of a visual layer
Colour Shift properties are:
Brightness (shift)
Section titled “Brightness (shift)”Changes the floor of brightness to the constant given.
When set to 0, the range of brightness is 0 to 1, thus no change is applied to the image. When set to -1, the range of brightness is -1 to 0, thus the entire image is black. When set to 1, the range of brightness is 1 to 2, thus the entire image is white.
 Brightness (shift) (from left to right): -1, -0.5, 0, 0.5, 1
Brightness (shift) (from left to right): -1, -0.5, 0, 0.5, 1
Contrast (scale)
Section titled “Contrast (scale)”When set to 1, no change is applied to the image. When set to 0, all values have been pulled together to 50% grey, thus the image is entirely grey. When set to 2, the values are pulled in the opposite direction to meeting at mid grey, thus resulting in crushed white and black values.
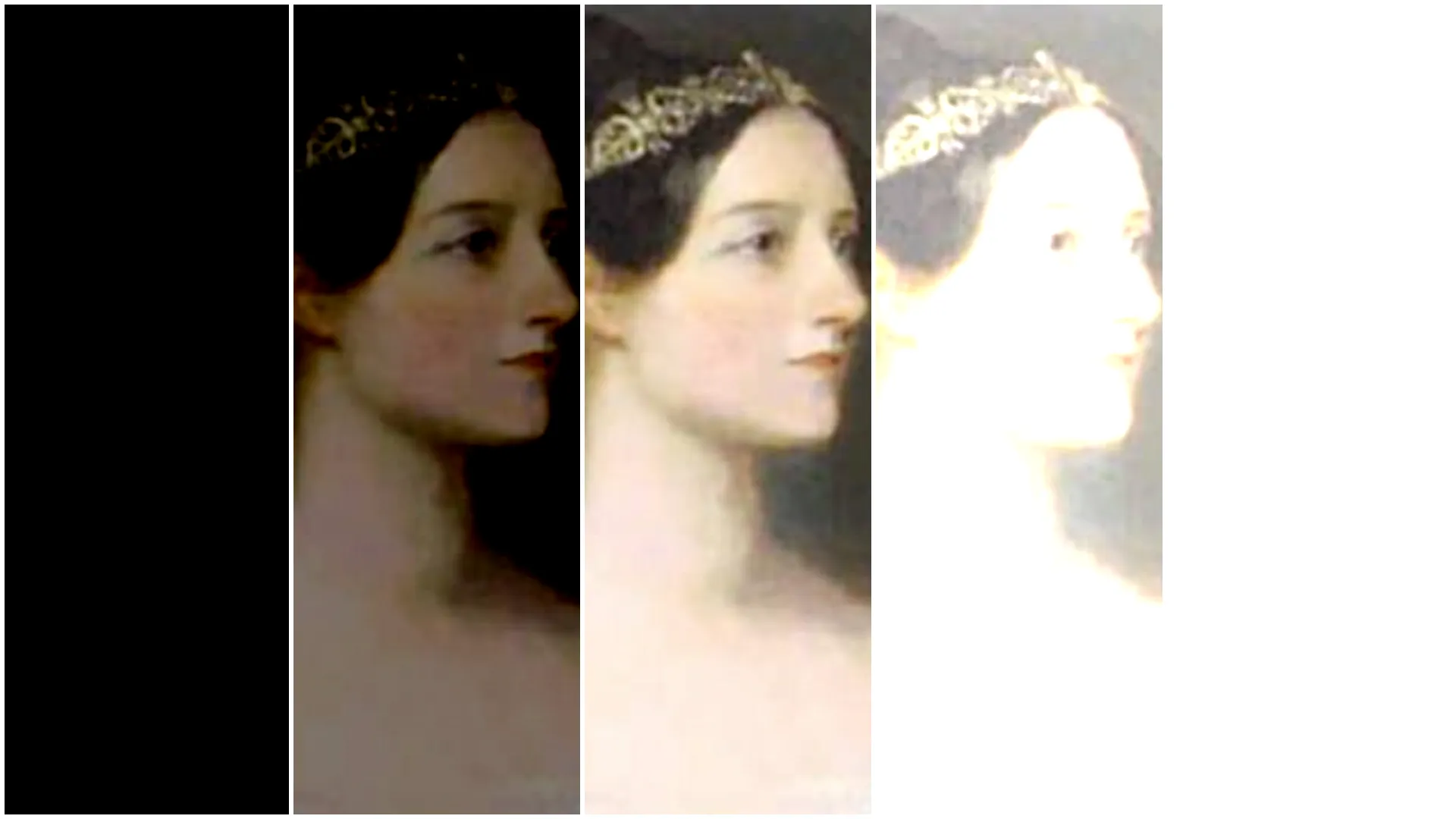
 Contrast (scale) (from left to right): 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2
Contrast (scale) (from left to right): 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2
Saturation scale
Section titled “Saturation scale”When set to 1, no change is applied to the image. When set to 0, the image is desaturated to black and white. When set higher than 1, the image is hypersaturated.
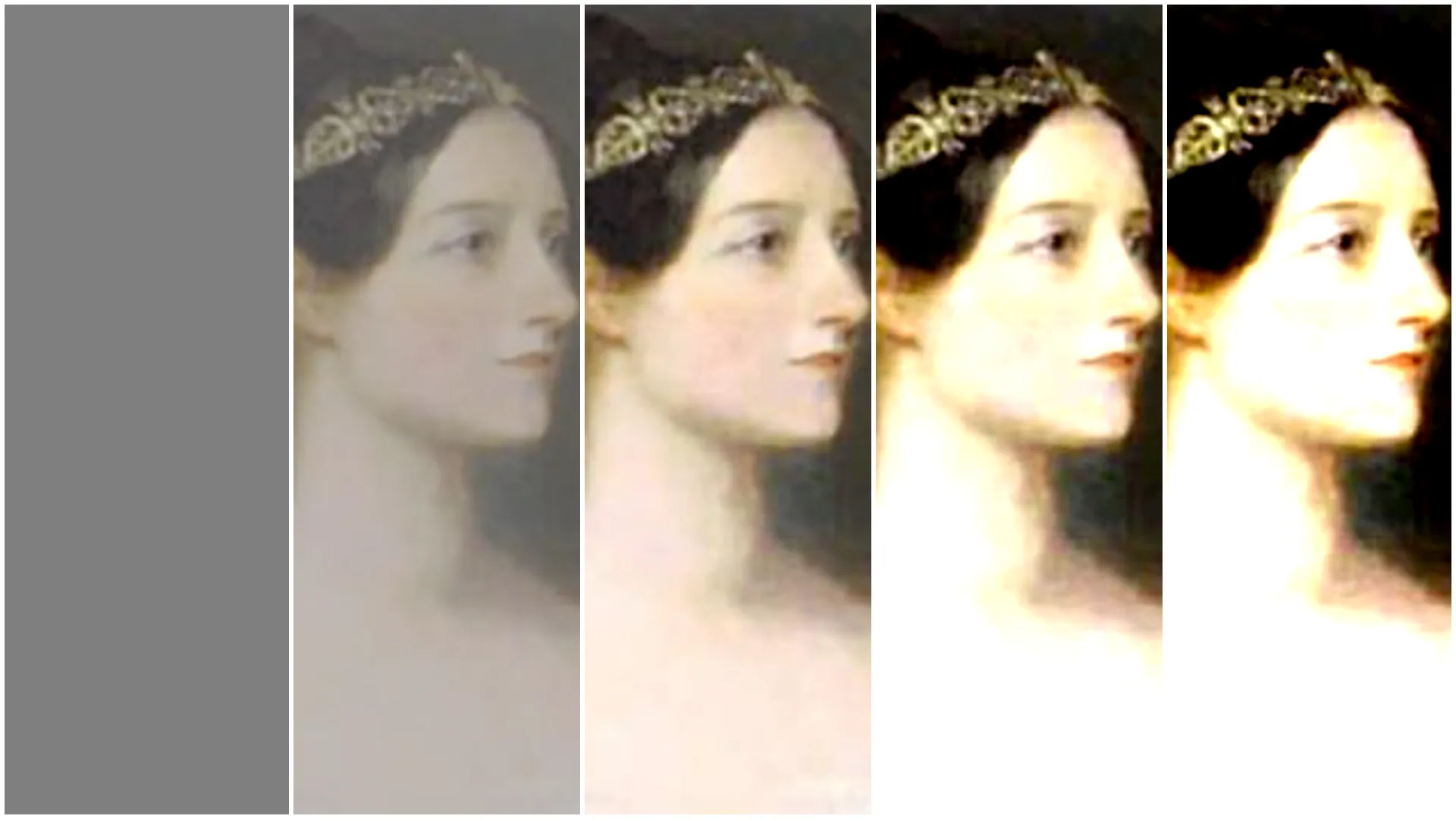
 Saturation scale (from left to right): 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4
Saturation scale (from left to right): 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4
Hue shift
Section titled “Hue shift”RGB controlled
Section titled “RGB controlled”This property controls how the min/max levels and gamma corrections are applied. If set to together, then the min, max and gamma values set for the red channel are mirrored to the green and blue channels, values set on the green and blue channels will be ignored. If set to separate , the min,max and gamma values can be controlled separately for red, green and blue. The latter setting allows you to apply fine colour balance controls to the image.
This sets the lowest brightness level found in the image. All pixels at this level are scaled down to zero brightness. Increasing this value enforces shadows and dark levels in the image and can be used to reduce low-level compression artifacts in an image or video frame.
Increasing min equally across red, green and blue enforces shadows, whereas increasing min on an individual channel has the effect of shifting the colour balance away from that colour. For example, increasing red min shifts the image towards cyan.
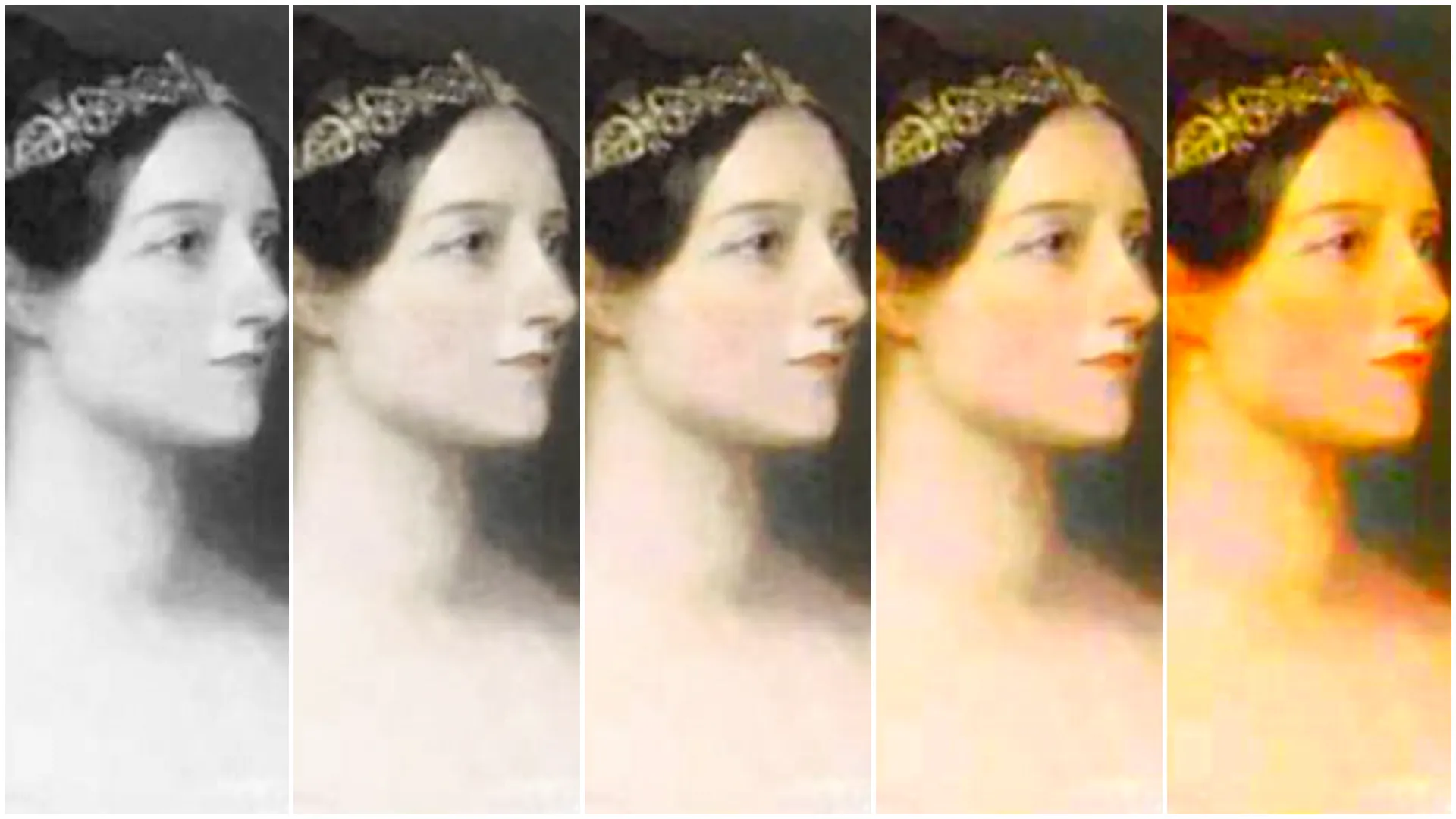
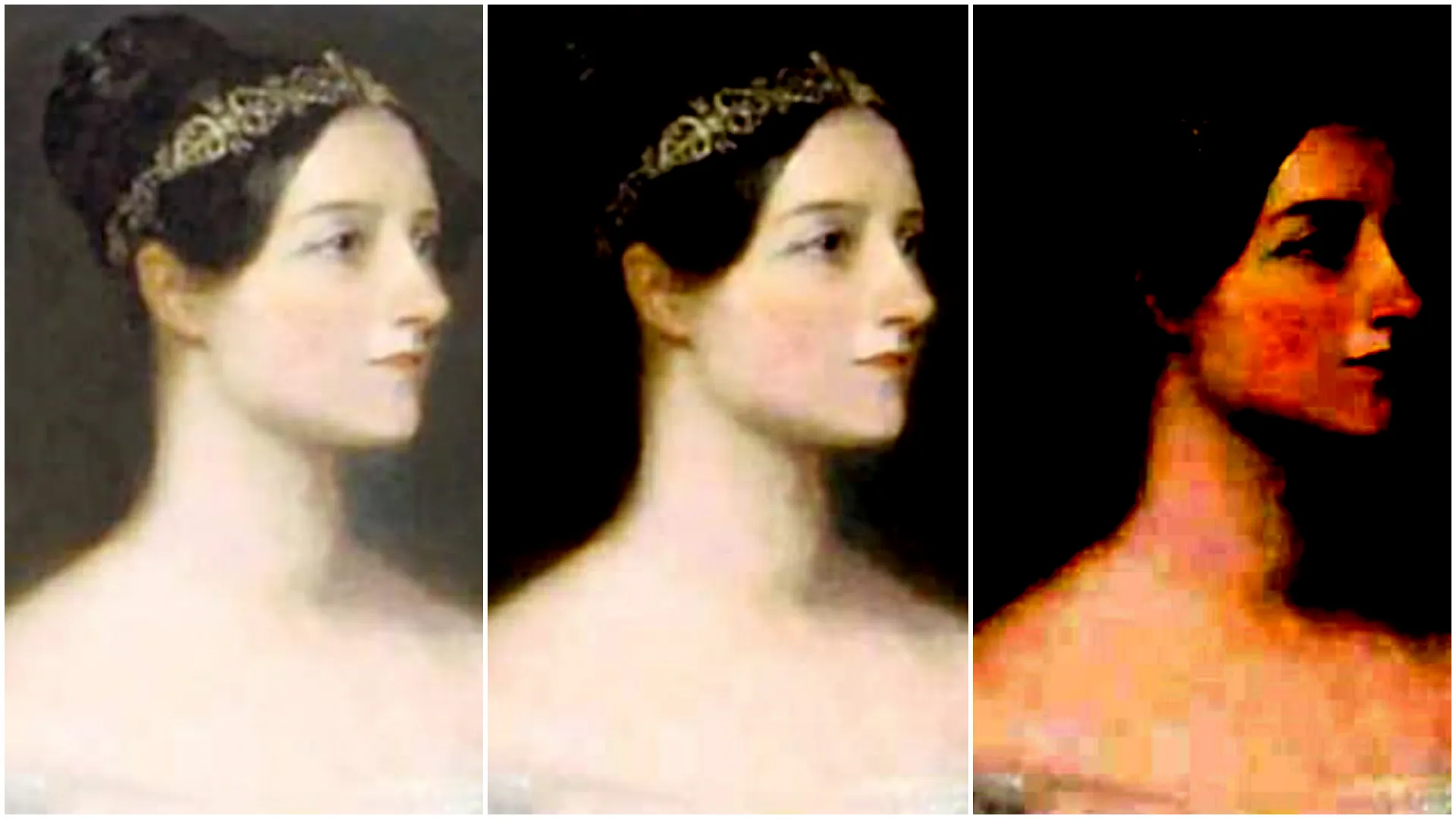 With
With RGB controlled set to Together (from left to right): 0, 0.3, 0.8
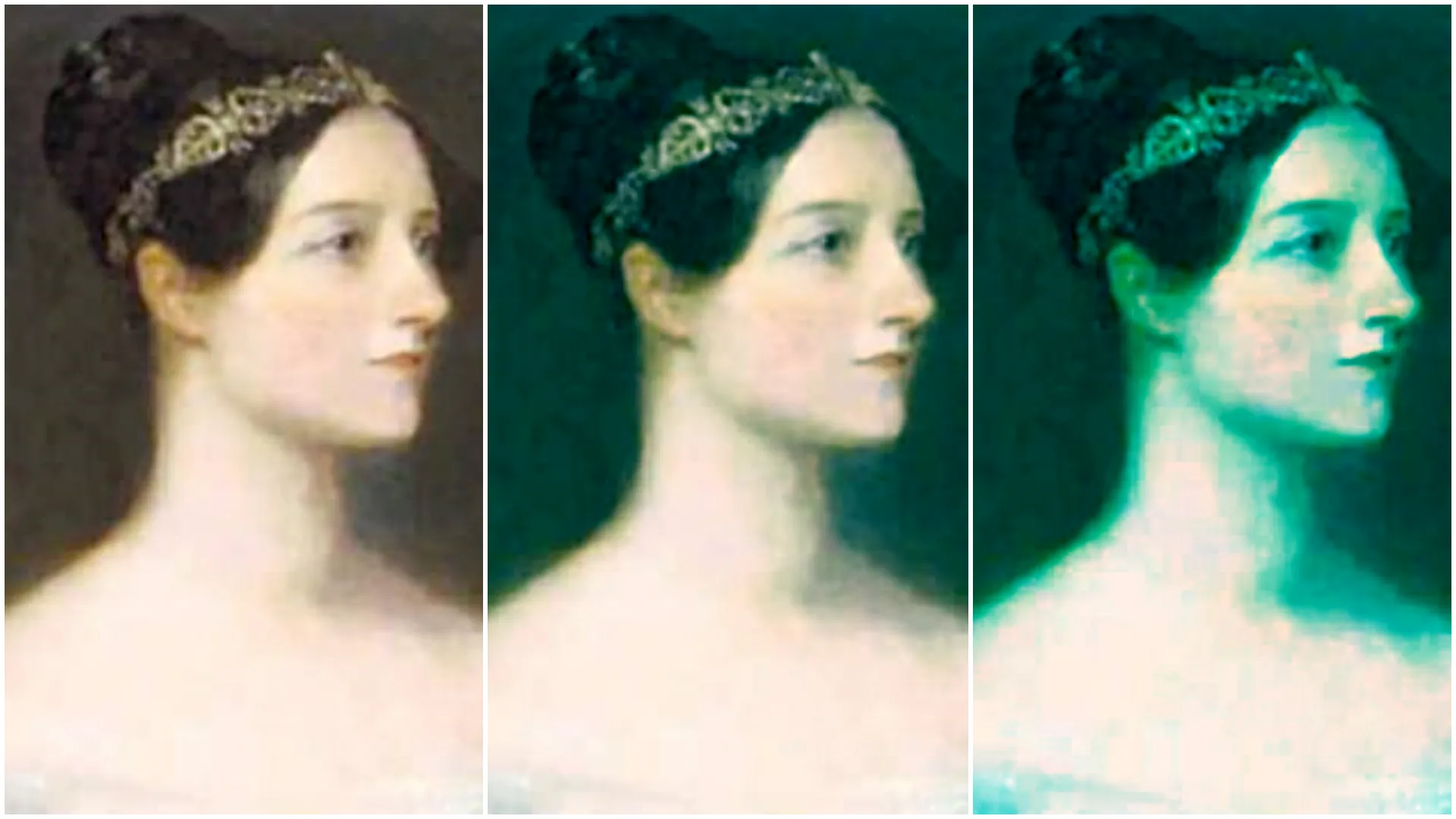 With
With RGB controlled set to Separate, red min (from left to right): 0, 0.3, 0.8
This sets the highest brightness level found in the image. All pixels at this level are scaled up to the maximumm level, i.e. 1. Decreasing this value brightens any highlights in the image. This is useful when the source image is too dark.
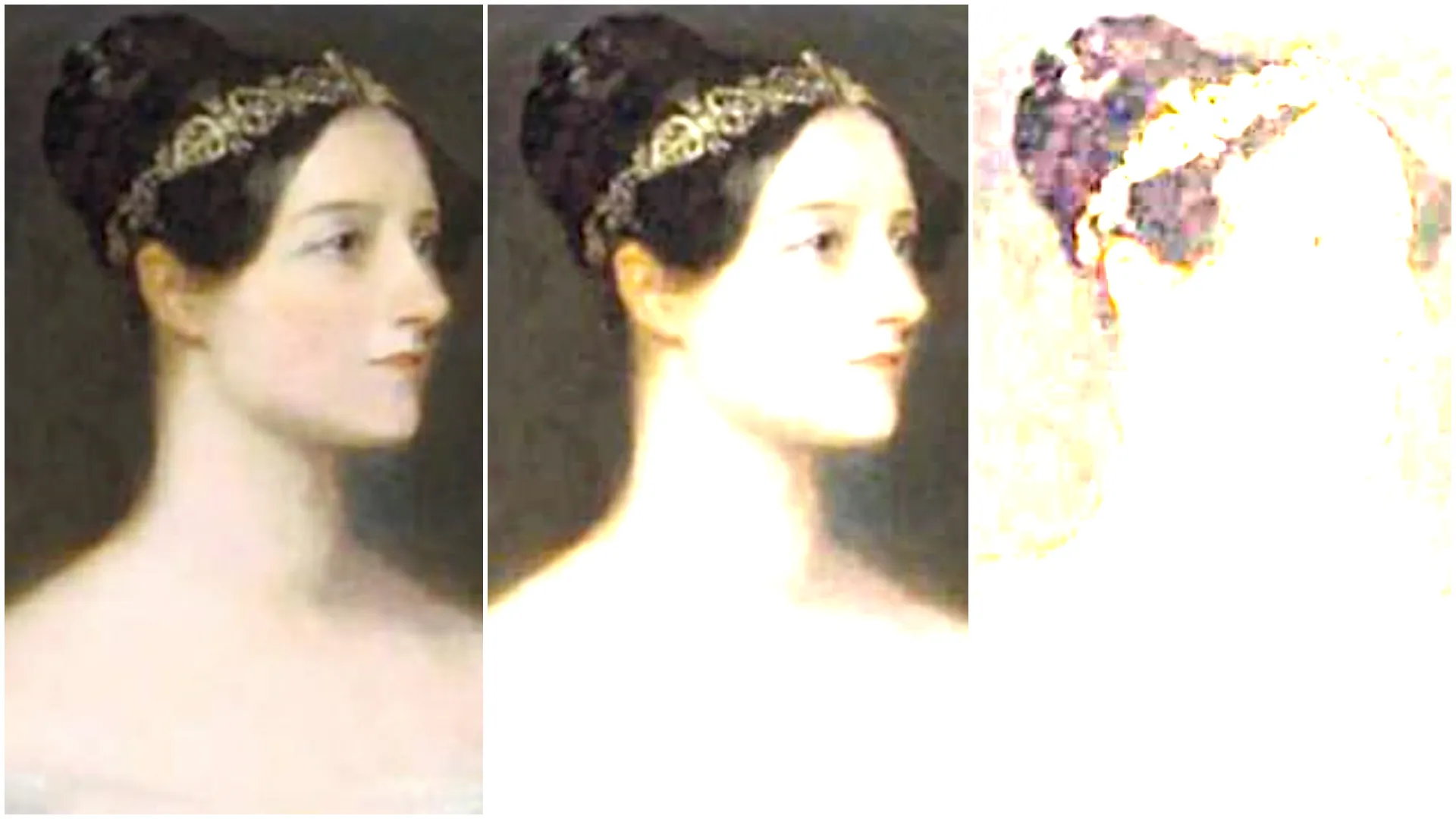 With
With RGB controlled set to Together (from left to right): 1, 0.7, 0.2
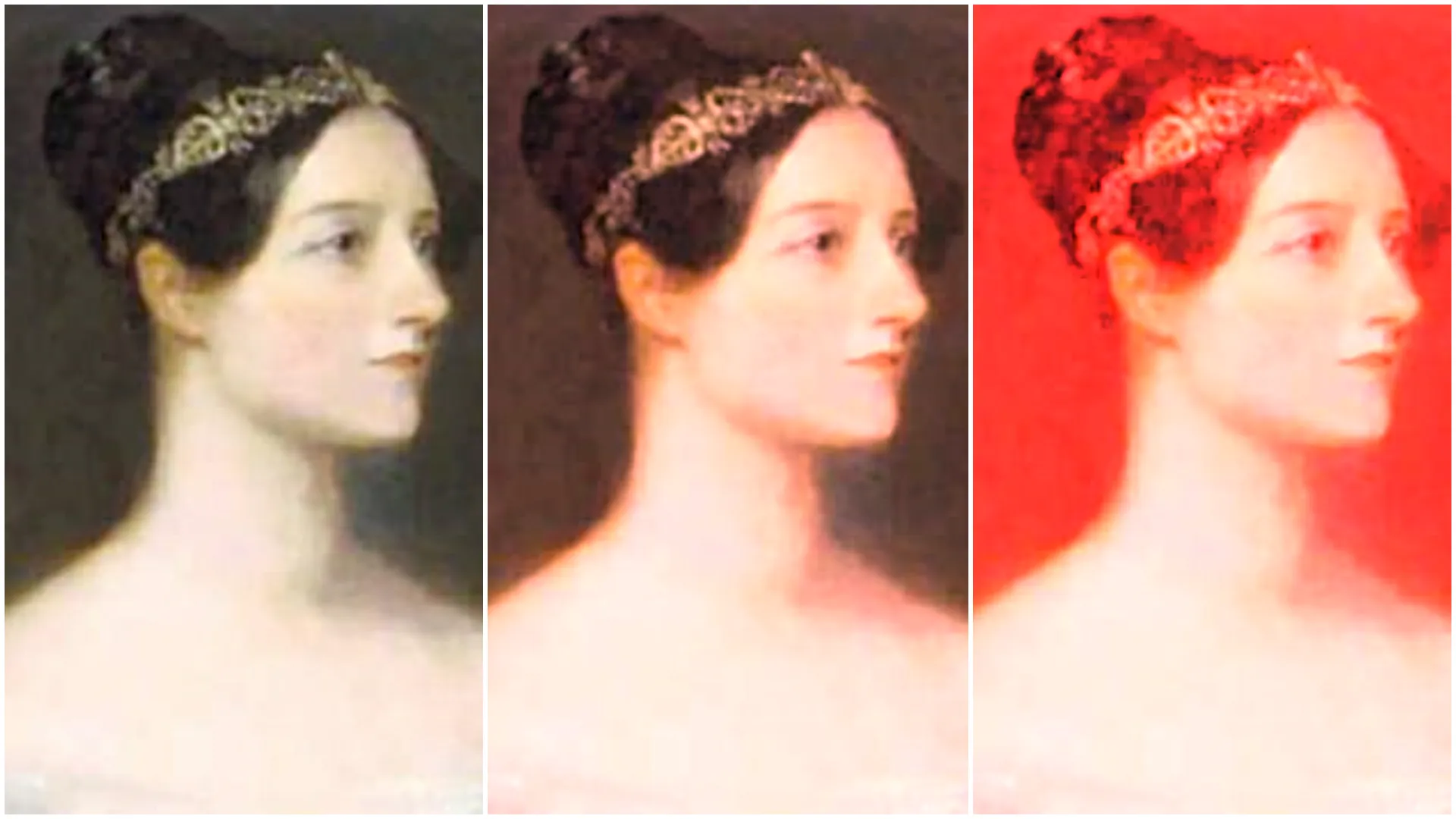 With
With RGB controlled set to Separate, red max (from left to right): 1, 0.7, 0.2
When gamma is set to 1, no change is made to the image. Reducing gamma brightens highlights while increasing gamma darkens lowlights. The maximum and minimum brightness levels remain the same.
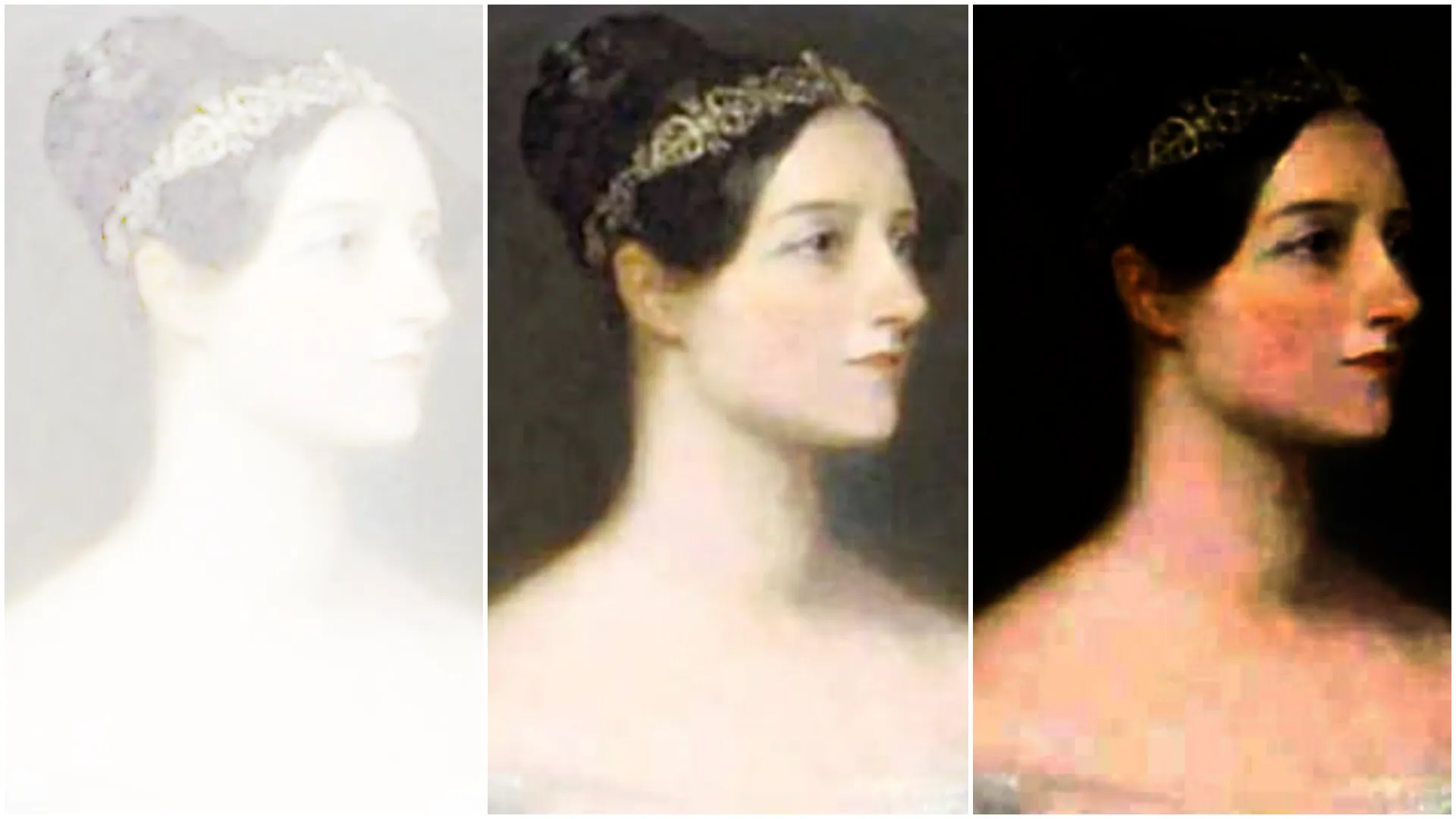 With
With RGB controlled set to Together (from left to right): 0.1, 1, 4
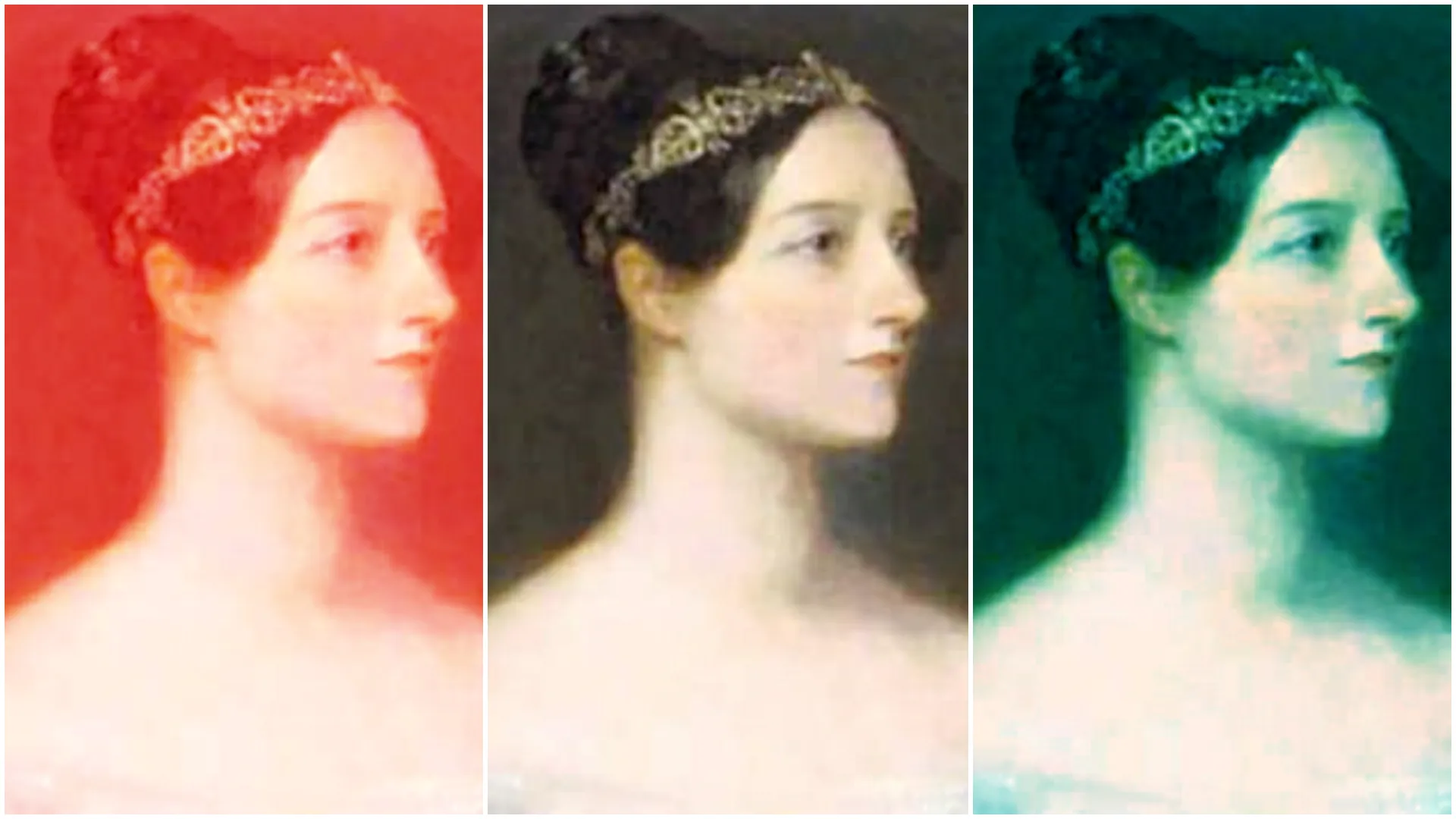 With
With RGB controlled set to Separate, red gamma (from left to right): 0.1, 1, 4