RAID Configuration
このコンテンツはまだ日本語訳がありません。
The drives used in this guide are examples only. Your system may differ. For guidance on required or recommended drives, contact the Disguise Support team.
Logging in to the RAID Controller
Section titled “Logging in to the RAID Controller”Before configuring RAID, ensure your Windows user account has a password set.
- Open the Windows Start Menu and select LSA.
- On the LSA landing page, select the server with your local IP address.
- Enter your login details of the local user account.
- Username:
d3 - Password: not set
- Username:
Viewing the RAID Configuration in LSA
Section titled “Viewing the RAID Configuration in LSA”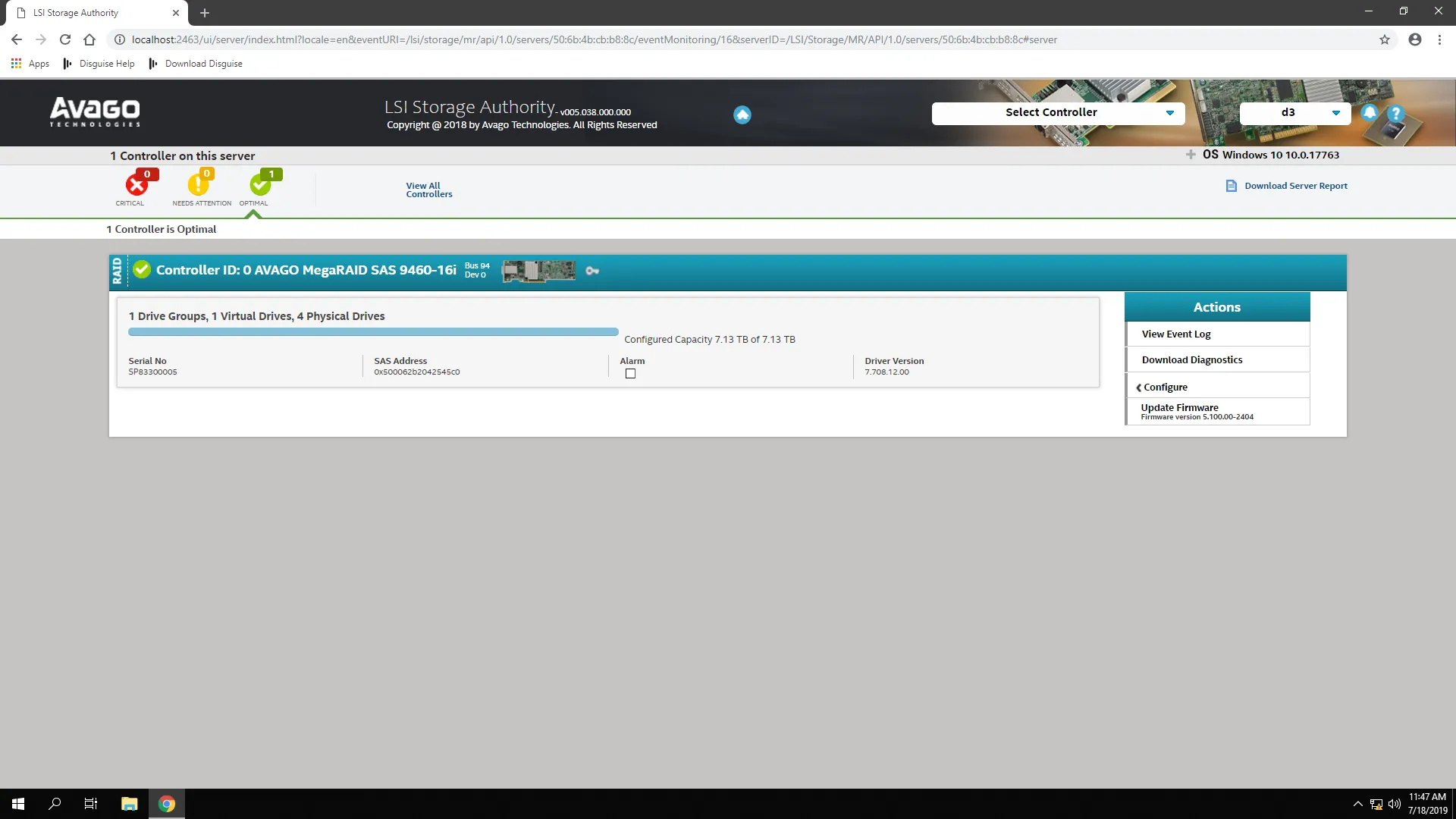
The landing page displays controller information, including system health, total capacity and detected drives.
- Open the Select Controller dropdown and choose your controller.
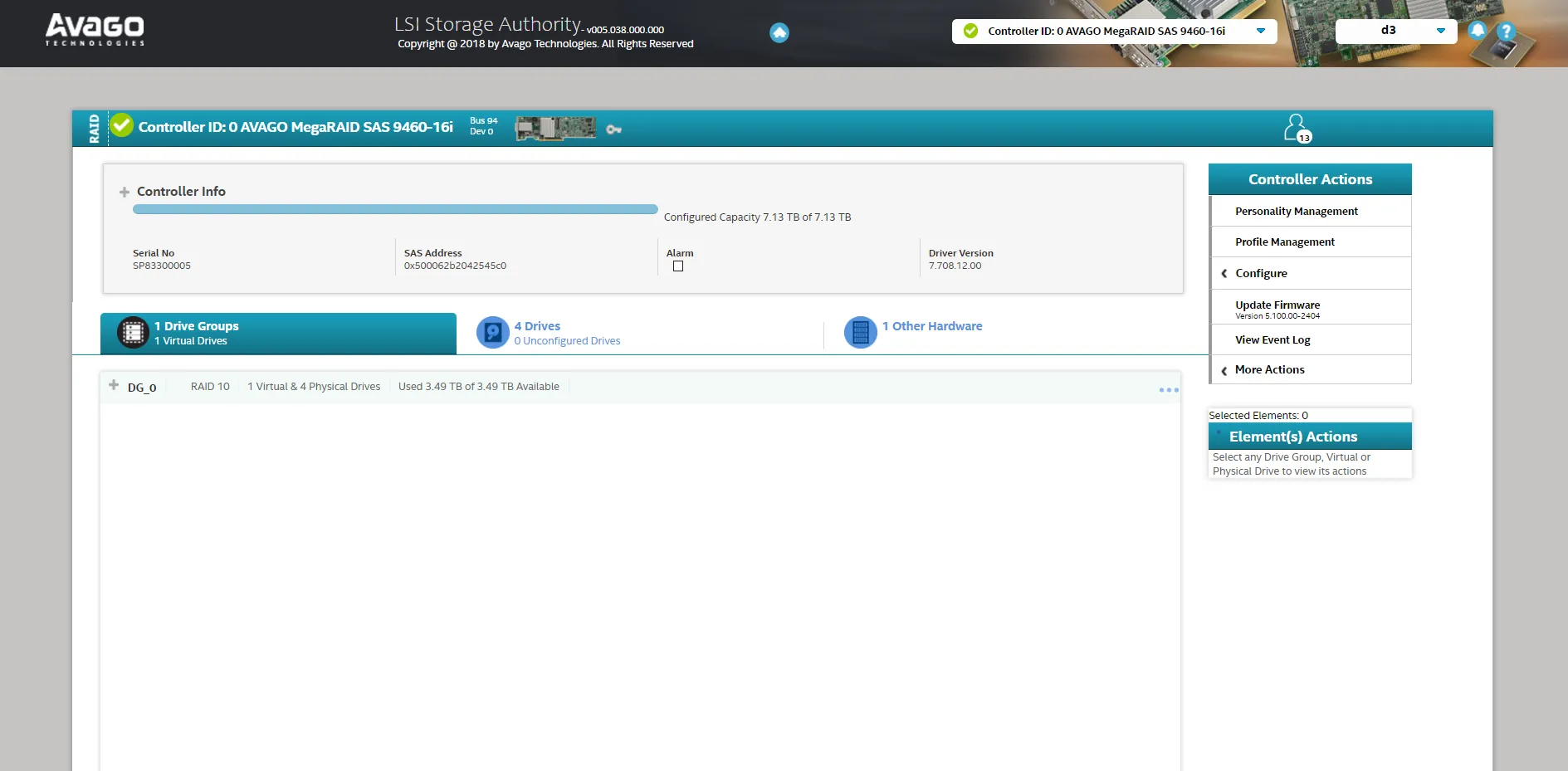
- Review the controller page for drive count, capacity, and status.
- Open the first tab to view detailed Virtual Drive information, such as RAID levels.
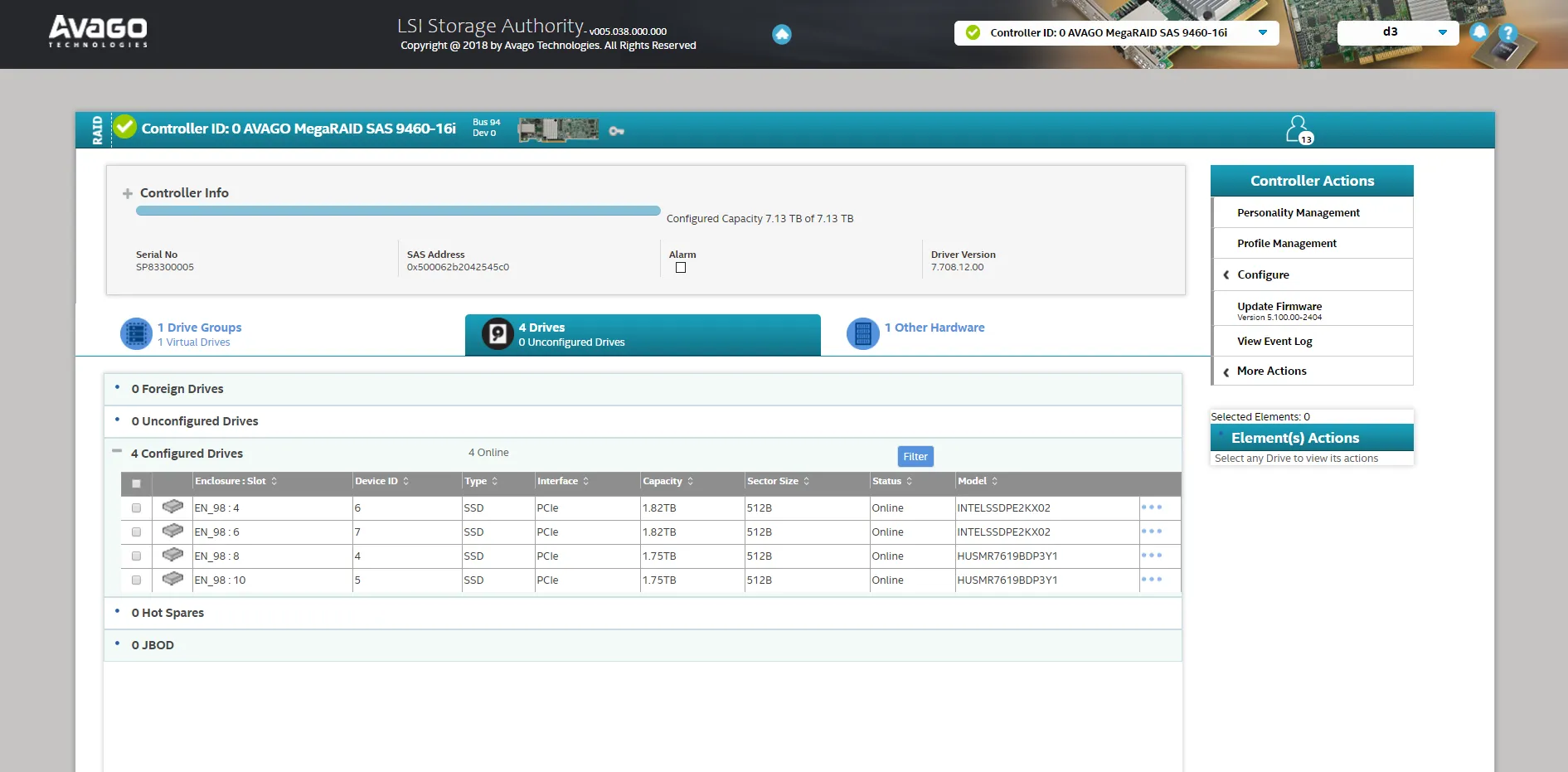
- Use this information to begin your configuration tasks.
Creating a RAID
Section titled “Creating a RAID”The following steps will take you through creating a RAID if no Virtual Drive already exists.
- Open the Configure tab.
- Select Advanced Configuration.
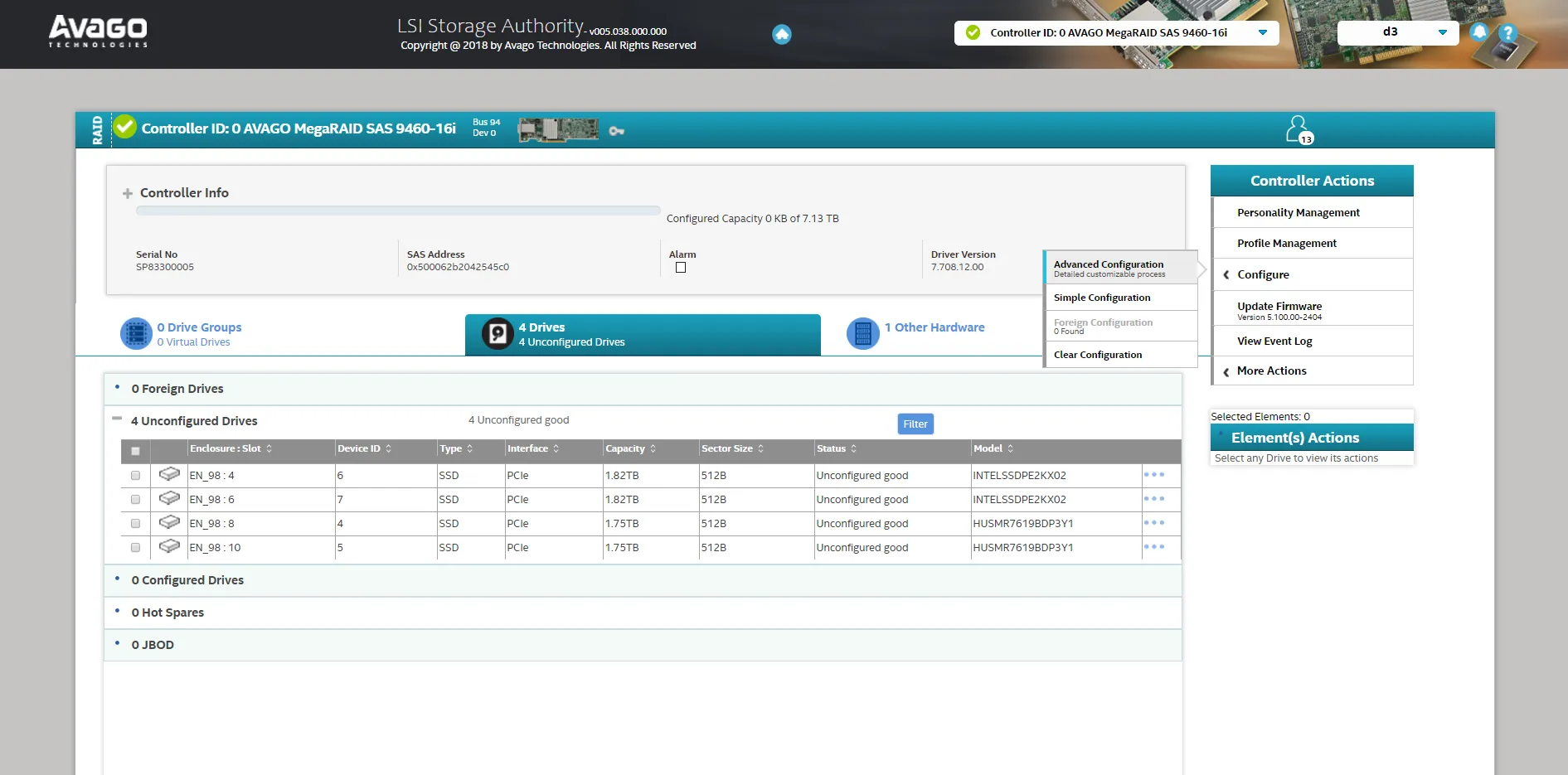
- Choose RAID 10, which is the recommended configuration. This is selected to meet any performance stats released by Disguise. If the RAID is set up at a different level, you could be at risk of losing your data without redundancy.
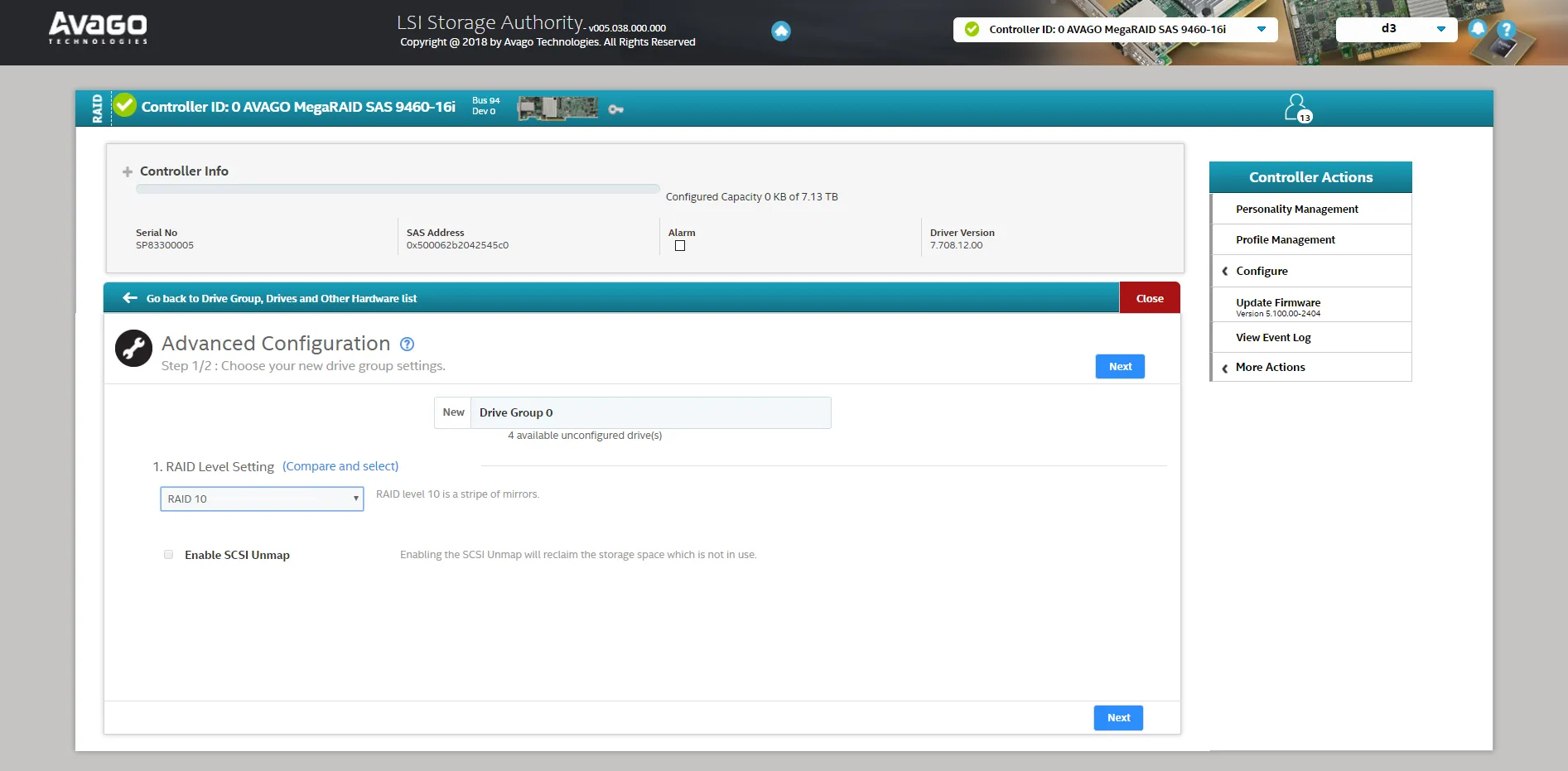
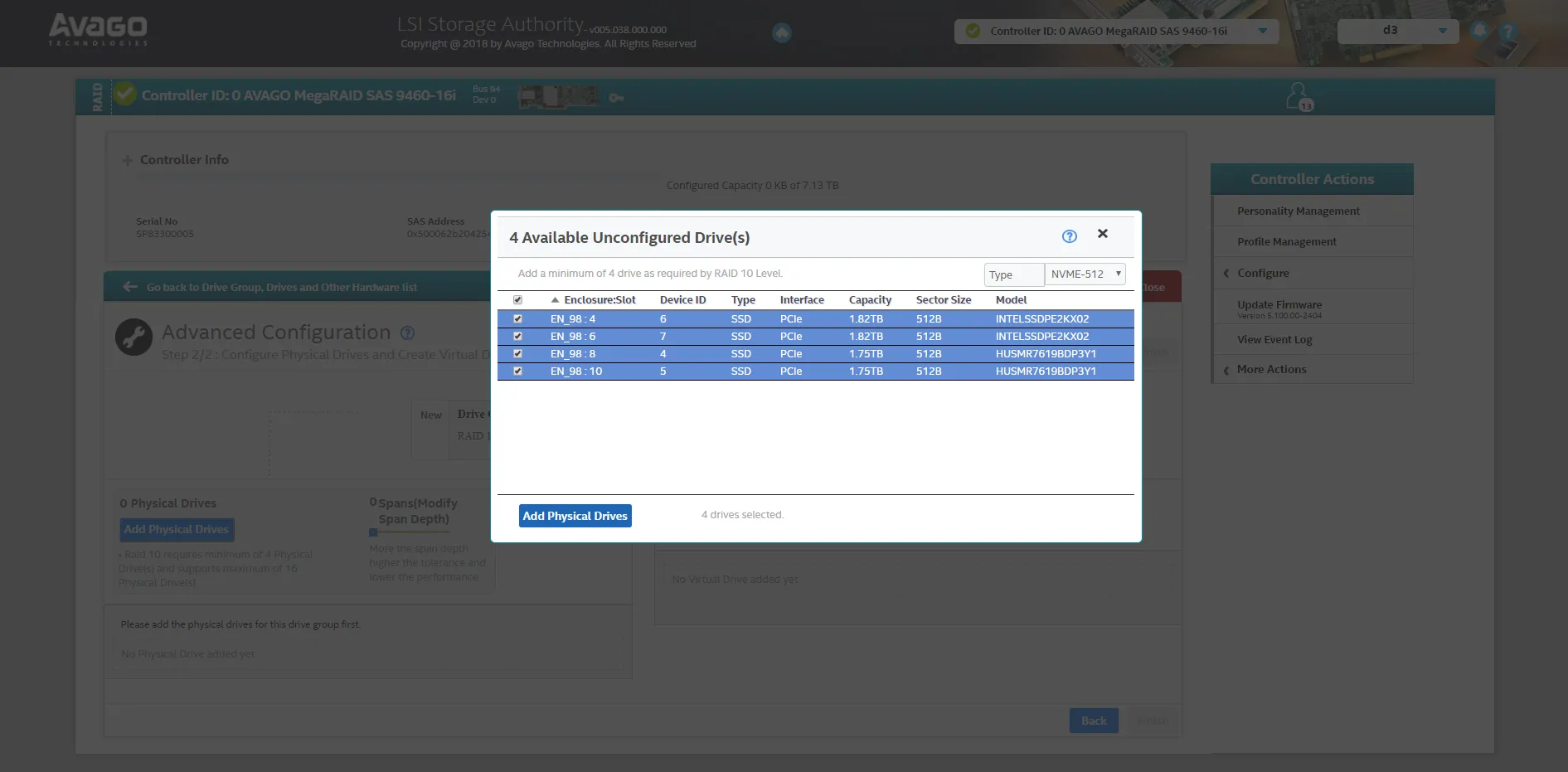
- Continue to the next page and select Add Physical Drives to choose which drives you are going to put into an array. RAID 10 requires a minimum of 4 drives to be set up
- Select Create Virtual Drive, then apply the following settings:
- Virtual Drive Name: Media
- Strip Size: 256 KB
- Initialization State: No Initialization
- Read Policy: Always Read Ahead
- Write Policy: Write Through
- I/O Policy: Direct IO
- Disk Cache Policy: Unchanged
- Select Create Virtual Drives.
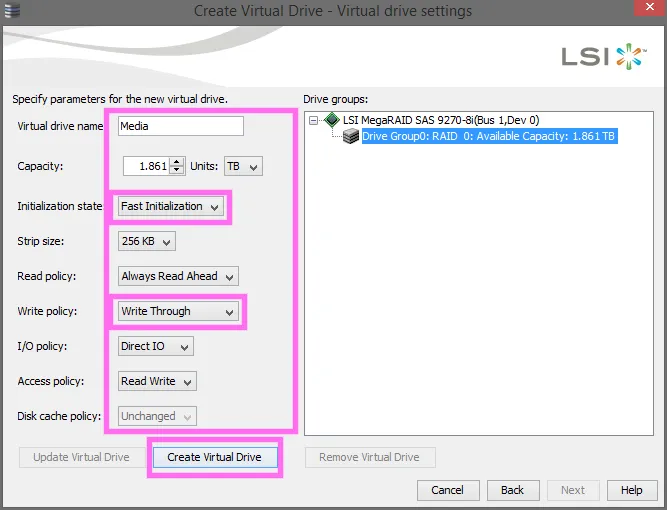
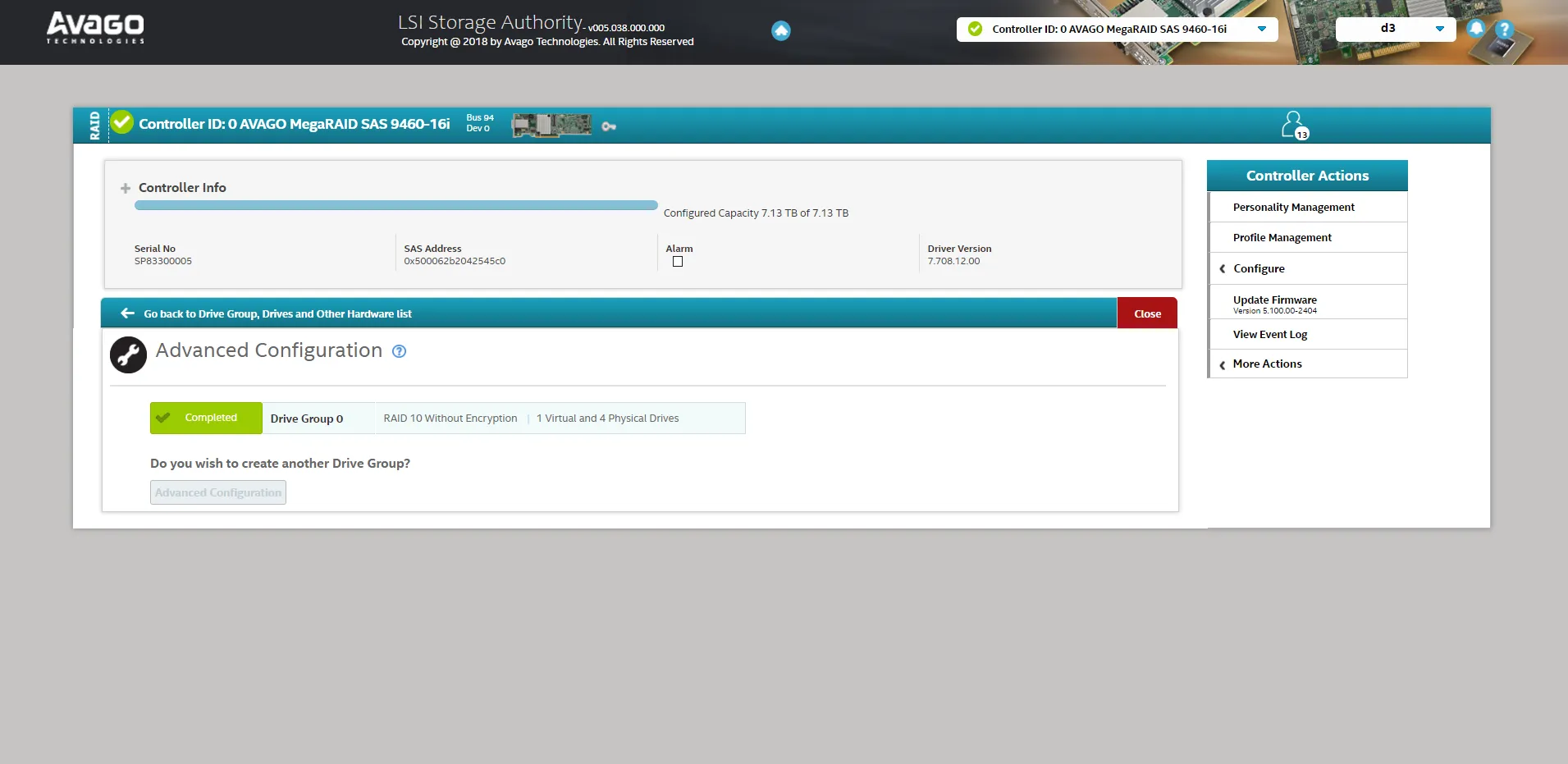
- Select Finish to complete the process.
- Review the completion page for RAID details.
Replacing an existing Virtual Drive
Section titled “Replacing an existing Virtual Drive”To replace an existing Virtual Drive with a new Drive, delete the existing drive and then create a new Virtual Drive:
- Launch LSA.
- User:
d3 - Password: n/a
- User:
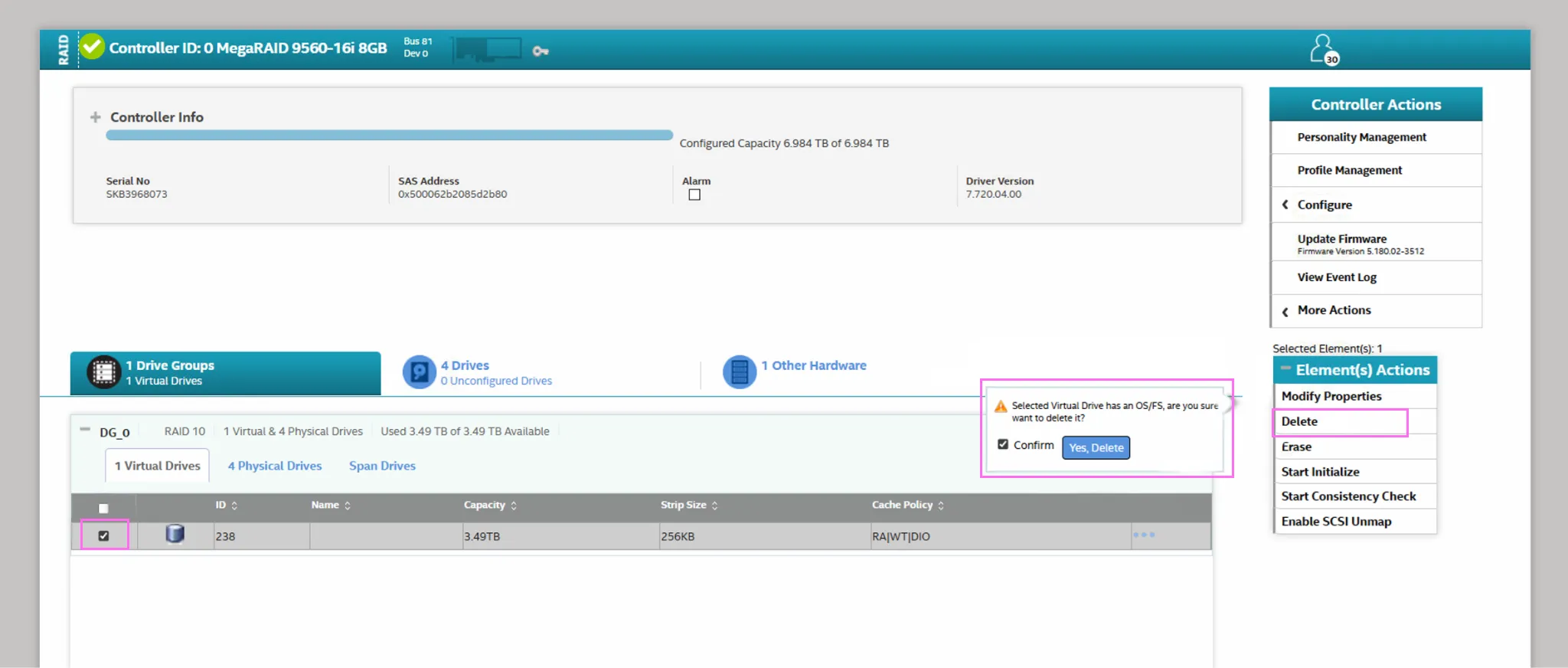
- Under Drive Groups, tick the checkbox to select the drive, and then select Delete from the Element(s) Actions.
- Select the physical drives to include in the new array.
- Select Add Virtual Drives, then apply the following settings:
- Virtual Drive Name - Media
- Strip size - 256 KB
- Initialization State - No Initialization
- Read Policy - Always Read Ahead
- Write Policy - Write Through
- I/O Policy - Direct IO
- Disk Cache Policy - Unchanged
- Click Add Virtual Drives.
- Select Finish to complete the process.
- Windows will prompt you to format and partition the new virtual drive. You may also do this manually if required. See the Manually format and partition on Windows section below for details.

- User the following format settings:
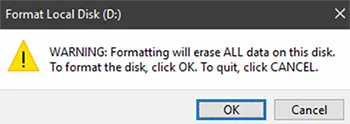
Capacity - DefaultFile System - NTFSAllocation unit size - Default allocation sizeVolume Label - You can leave this blank (‘D:’ is the default)Format options - Quick format since the RAID controller already handled drive initialization and health checks.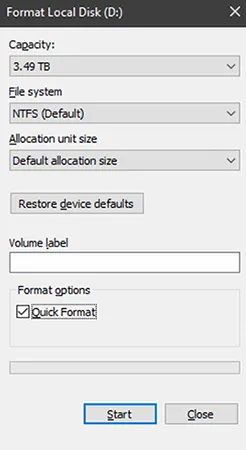 9. Click OK to confirm and close the Windows warning and finish formatting.
9. Click OK to confirm and close the Windows warning and finish formatting.
 20S. Congratulations, you now have a new RAID10 array. Open d3Manager and update the d3Project folder location if prompted. The common path is: C:\Users\User\Documents\d3 Projects.
20S. Congratulations, you now have a new RAID10 array. Open d3Manager and update the d3Project folder location if prompted. The common path is: C:\Users\User\Documents\d3 Projects.
Unconfigured Good/Bad
Section titled “Unconfigured Good/Bad”When replacing a physical drive, the LSI controller automatically detects the new disk. Before adding a drive to a RAID array, ensure it is marked Unconfigured Good.
If a drive is marked Unconfigured Bad, it must be converted first.
- Identify any drives marked Unconfigured Good - these are immediately ready for RAID configuration.
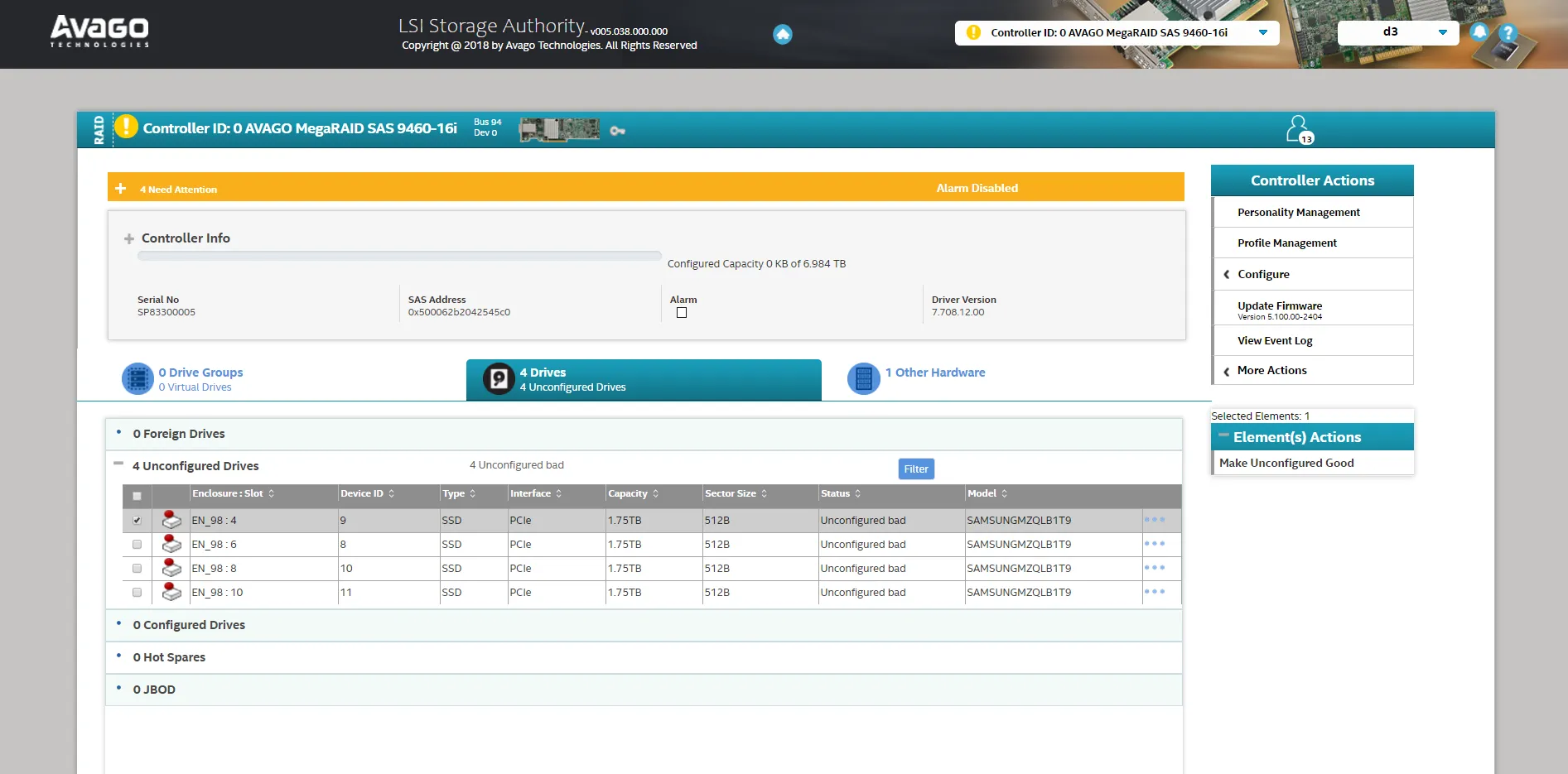
- For any drives marked Unconfigured Bad, select each drive individually.
- Under Element(s) Actions, choose Make Unconfigured Good.
Importing Foreign Configurations
Section titled “Importing Foreign Configurations”Drives previously used in another system, or recently changed from Unconfigured Bad, may show a Foreign Configuration. Foreign configurations must be reviewed and imported before the RAID can operate correctly.
- In the drive list, select any drives marked Foreign Drives.
- Navigate to Configure > Foreign Configuration
- Select Import to adopt the foreign configuration.
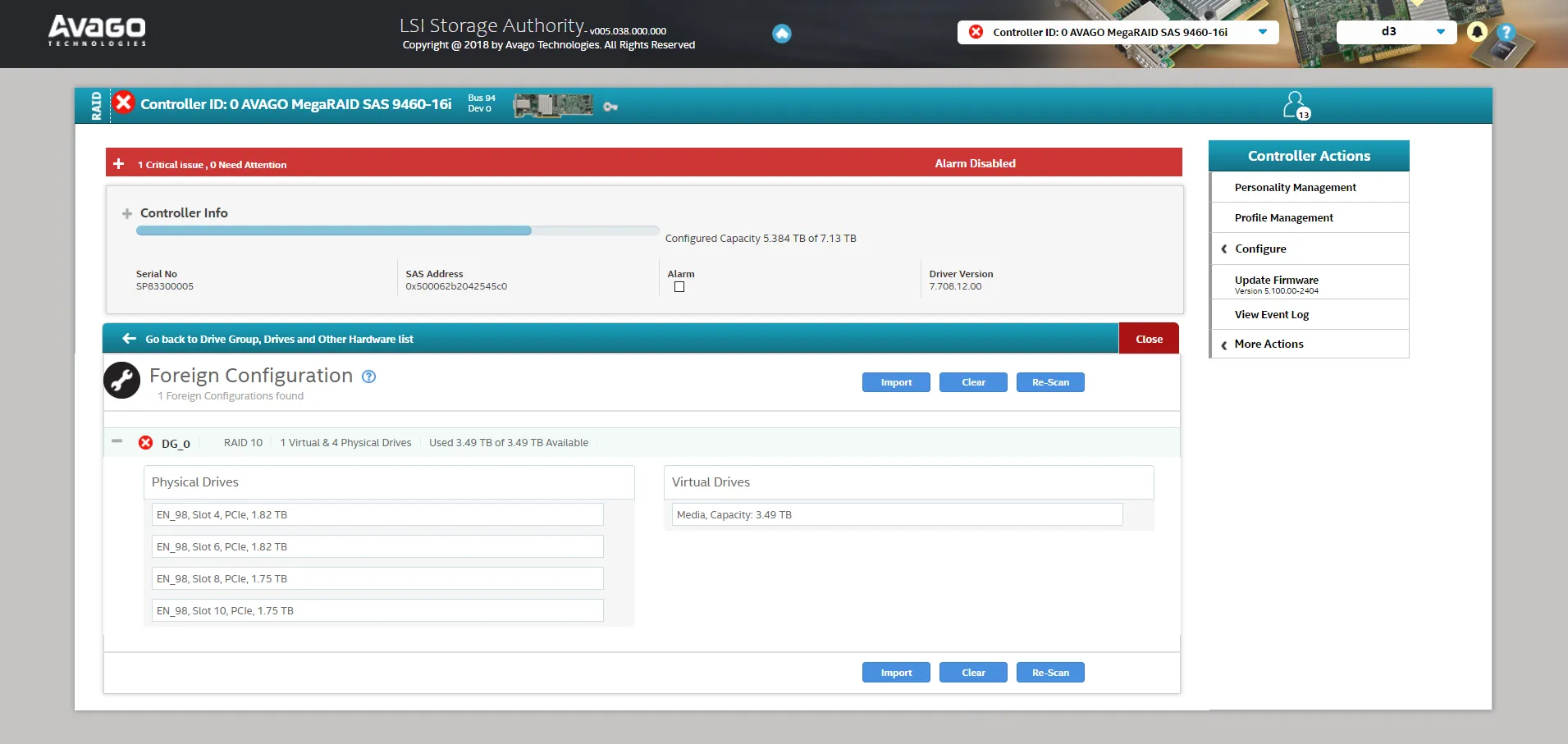
- Review the details of the Virtual Drive to confirm the import was successful.
Manually format and partition on Windows
Section titled “Manually format and partition on Windows”- Press the Start button.
- Type Disk Management and open Create and format hard disk partitions.
- In the lower panel, find the disk that represents your RAID virtual drive.
- If prompted to initialise the disk, choose GPT → OK.
- If no prompt appears, right-click the disk label (e.g., Disk 1) → Initialize Disk → select GPT → OK.
- In the unallocated area, right-click and choose New Simple Volume.
- Select the default full size.
- Choose a drive letter (e.g., D:).
- Use the following format settings:
File system: NTFSAllocation unit size: DefaultVolume label: (any name you want)Check “Perform a quick format”
- Click Next, then click Finish.