Migrating Porta On Prem WSL data to a new location
このコンテンツはまだ日本語訳がありません。
This guide will walk you through migrating the WSL virtual disk for Porta On Prem to a new location on your system.
1. Backup the virtual disk
Section titled “1. Backup the virtual disk”First, we want to create a database backup to ensure we have a restore point in case anything goes wrong.
- Use the system tray to shut down Docker Desktop.
- After Docker has finished shutting down, open Powershell.
- Run
wsl --shutdownto stop all distributions. - Run
wsl -l -vand ensure the docker distros are stopped. A successful output will look like this:NAME STATE VERSION* Ubuntu-22.04 Stopped 2docker-desktop-data Stopped 2docker-desktop Stopped 2 - Export the
docker-desktop-datadistribution to a.tarfile.-
Open powershell as an administrator.
-
Confirm that
docker-desktop-dataexists and is stopped by running:wsl -l -vA successful output will look like this:
NAME STATE VERSION* Ubuntu-22.04 Stopped 2docker-desktop-data Stopped 2docker-desktop Stopped 2 -
In Powershell, run the following command to export the
docker-desktop-datadistribution to a.tarfile.- In the command, replace
D:\path\to\backupwith your desired backup directory.- This directory must already exist prior to exporting. Create a new directory if necessary.
- Make sure the export destination has enough free disk space.
- The export may take a while if the virtual disk is large (anywhere from 5 to 15 minutes).
-
Terminal window wsl --export docker-desktop-data D:\path\to\backup\docker-desktop-data.tar
- In the command, replace
-
You’ll know the export has finished when the
PS C:\Users\username>prompt appears again on the next line.
-
- Verify the backup file was created successfully.
- Navigate to the backup directory you specified in step 2.
- Confirm that the
docker-desktop-data.tarfile exists. - Check the file size to ensure it’s greater than 0 bytes.
2. Confirm that your target drive is formatted as NTFS
Section titled “2. Confirm that your target drive is formatted as NTFS”- In Explorer, navigate to
This PC. - Right-click the drive you want to restore to and select
propertiesfrom the context menu. - In the window that opens, check the
File systemproperty.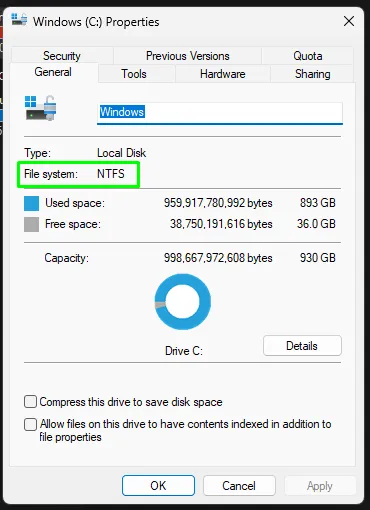
3. Locate your existing virtual disk
Section titled “3. Locate your existing virtual disk”- In Explorer, navigate to
%LOCALAPPDATA%\Docker\wsl\datato find your existing virtual disk file, namedext4.vhdx. - You can also check Docker Desktop’s Settings > Resources > Advanced and check its
Disk image location.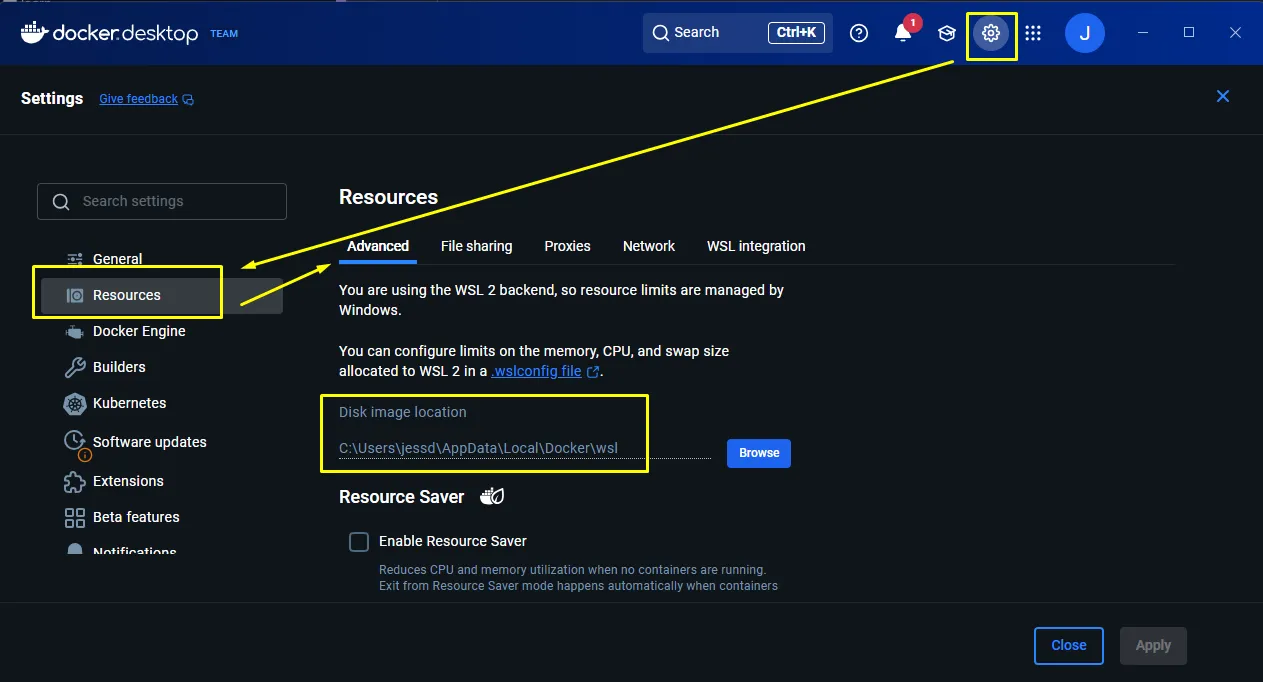
- Note this path so that we can copy it for use later.
4. Shut down Docker Desktop
Section titled “4. Shut down Docker Desktop”- Use the system tray to quit Docker Desktop.
- Open Powershell.
- Run
wsl --shutdownto stop all distributions. - Run
wsl -l -vand ensure the docker distros are stopped. A successful output will look like this:NAME STATE VERSION* Ubuntu-22.04 Stopped 2docker-desktop-data Stopped 2docker-desktop Stopped 2
5. Unregister (delete) the existing docker-desktop-data distribution
Section titled “5. Unregister (delete) the existing docker-desktop-data distribution”-
Open Powershell as an administrator.
-
Confirm that
docker-desktop-dataexists and is stopped by running:wsl -l -vA successful output will look like this:
NAME STATE VERSION* Ubuntu-22.04 Stopped 2docker-desktop-data Stopped 2docker-desktop Stopped 2 -
In Powershell, run the following command to unregister (delete) the
docker-desktop-datadistribution:wsl --unregister docker-desktop-data -
You will not receive any confirmation message, but you can verify it was removed by running
wsl -l -vagain.- The output should no longer list
docker-desktop-data:
NAME STATE VERSION* Ubuntu-22.04 Stopped 2docker-desktop Stopped 2 - The output should no longer list
-
You can also check the disk location in Windows explorer (likely
%LOCALAPPDATA%\Docker\wsl\data) to ensure that theext4.vhdxfile was removed.
6. Restore the virtual disk to the new location
Section titled “6. Restore the virtual disk to the new location”Now that we have a backup, we can proceed to restore the virtual disk to the new location.
-
Ensure that the folder that you will be restoring your data to already exists, e.g.,
%LOCALAPPDATA%\Docker\wsl\data, orD:\wsl\docker-desktop-data. -
Import the data to restore the
docker-desktop-datadistribution from your backup.tarfile.- Open Powershell.
- Run the following command to import the backup.
- Replace
D:\path\to\backupwith the path to your backup file. - Replace
D:\path\to\restore\folderwith the path to your restore destination directory.
Terminal window wsl --import docker-desktop-data "D:\path\to\restore\folder" "D:\path\to\backup\docker-desktop-data.tar" --version 2 - Replace
- You’ll know the import has finished when the
PS C:\Users\username>prompt appears again on the next line.
-
After the import has finished, confirm that the distro is recognized in WSL by opening Powershell and running:
wsl -l -vA successful output will look like this:
NAME STATE VERSION* Ubuntu-22.04 Stopped 2docker-desktop-data Stopped 2docker-desktop Stopped 2 -
Start Docker Desktop again. It should find and use the newly imported
docker-desktop-datadistribution. -
After starting Docker, in Powershell, run a quick
docker imagesordocker volume lscommand to confirm your images/volumes are still present. -
Everything should be back to normal now.